Ethereum 2.0 is set to launch on the 1st of December, and using this as an excuse I decided to invest some time to learn a bit more about the new developments happening in the Ethereum space.
What is Eth2?
Eth2 refers to a set of interconnected upgrades that will make Ethereum more scalable, more secure, and more sustainable. These upgrades are being built by multiple teams from across the Ethereum ecosystem.
Before we jump into describing what is Ethereum 2.0 all about. Why does Ethereum need an upgrade in the first place? Is something wrong with the current network? The main reasons driving these changes are: Ethereum’s high demand --pushed even further by the DeFi fever-- which is driving up transaction fees and making the network intractable for average users; the disk space needed to run an Ethereum client which is growing at a fast rate; and the seek for a secure and sustainable underlying consensus algorithm that removes the large amounts of electricity --with its consequent environmental impact-- required to validate blocks in the network.
If we had to summarize Ethereum 2.0 in a sentence we could say that it is “an upgrade to implement a Proof of Stake Ethereum with shards”. The roadmap of the project has been divided in the phases depicted in the image below:
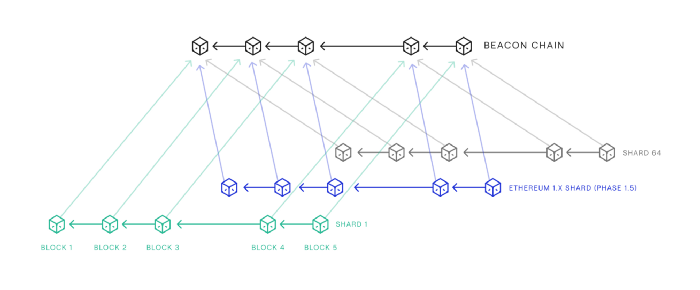
Phase 0 - Beacon Chain
This is the phase that is launching the 1st of December and it sets the stage for the transition of Ethereum from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake. In Phase 0 the beacon chain is released. The beacon chain is the entity that will be responsible in following phases for orchestrating the consensus between the different shards (and thus enforcing the security of the full network).
The operation of the Beacon Chain is (at least initially) simple, it randomly selects between a pool of validators the next node entitled to validate a new block. Nodes in the Beacon Chain need to stake 32 ETH to become validators. Before the Beacon Chain could be successfully shipped, 524,288 ETH had to be staked in the staking deposit contract. This milestone was reached at the beginning of this week (leaving the way clear for its release on the first day of December).
This phase is meant to allow enough time for the new consensus model to gather ETH deposits in the staking contract and node participation for the phases to come. This ensures that the security of the blockchain is never compromised when the time comes to gradually start turning off the PoW consensus and have the new PoS “Casper FFG” mechanism fully take over.
Phase 1 - Shard Chains
Phase 1 will serve as the implementation process of the shard chains. Shard chains are designed to run as interconnected blockchains that share the load of transactions on the Ethereum ecosystem. Once these shards are fully functional, all nodes will only have to download the transaction history of a subset of shards to engage and execute transactions on the Ethereum network. This approach is less cumbersome than the current design that requires nodes or clients to download the history of the entire network.
In Phase 1, a total of 64 PoS-enabled shards are planned. However, they will not support smart contracts and accounts at this time. Initially shards will just provide extra data to the network. They won’t handle transactions or smart contracts. Shards will use L2 technologies such as rollups to bundle several transactions in the same cryptographic proof and then submit it to the chain. This will reduce the data needed for a transaction, and the number of transactions, because a single Ethereum transaction is in reality the bundle of thousands of transactions.
With shards is when Ethereum scaling really starts. Even without the ability of performing executions shards will provide incredible improvements to transactions per second when combined with rollups.
“The plan was always to add extra functionality to shards, to make them more like the Ethereum mainnet today. This would allow them to store and execute smart contracts and handle accounts. But considering the transactions per second boost that version 1 shards provide, does this still need to happen? This is still being debated in the community and it seems like there are a few options.”
Phase 1.5 - Docking mainnet with Eth2
With Phase 1.5 mining will come to an end, and only PoS validators will see to the day-to-day validation needs of the Ethereum ecosystem. The current Eth1 mainnet will become just another shard. Ethereum mainnet will continue to be secured by proof-of-work , even while the Beacon Chain and its shard chains run in parallel using proof of stake . The docking is when these two systems are merged together. This will signal the end of proof-of-work for Ethereum and start the era of a more sustainable, eco-friendly Ethereum. At this point Ethereum would have solved the scalability, security and sustainability issues outlined above.
“Eventually the current Ethereum mainnet will "dock" with the rest of the Eth2 upgrades. Imagine Ethereum is a spaceship that isn’t quite ready for an interstellar voyage. With the Beacon Chain and the shard chains the community has built a new engine and a hardened hull. When it’s time, the current ship will dock with this new system so it can become one ship, ready to put in some serious lightyears and take on the universe.”
Phase 2 - Eth2 and beyond
Phase 2 is the last stage of the planned Ethereum 2.0 upgrade. Phase 2.0 will usher in fully functioning shard chains. In essence, these chains will start supporting accounts and contracts and, at the same time, communicate seamlessly.
Shard chains transition from simple data containers to a structured chain state and Smart Contracts will be reintroduced. Each shard will manage a virtual machine based on eWASM. It'll support accounts, contracts, state, and other abstractions that we’re familiar with from solidity. We can expect familiar tools like truffle, solc, ganache ported to support eWASM before or during Phase 2.
Phase 2 also introduces the concept of 'Execution Environments (EEs)'. EEs within a shard can be constructed in whatever way a developer sees fit - there could be an EE for a UTXO-style chain, a Libra-style system, an EE for a fee market relayer and beyond. Every shard has access to all execution environments and has the ability to make transactions within them as well as run and interact with smart contracts. Do note that the concept of execution environments is still in heavy research and development.
Launching a blockchain network ≈≈ 🚀
Launching a blockchain is like launching a software rocket!
I hope that after this introduction it has become clearer what Ethereum 2.0 is all about, and what to expect from the ecosystem in the near (and not that near) future. There is a growing analogy in the blockchain ecosystem where the teams developing the launch of complex next-generation blockchain networks, such as Ethereum 2.0 or Filecoin, say that launching a blockchain network is like launching a rocket, once it is live and in orbit there is nothing else you can do. I really like and agree with this analogy. Blockchain networks and protocols, like rockets, are complex systems with a lot of moving parts that need to be thoroughly tested to ensure their success. Once live, if something fails there is no easy way back. A rocket cost millions, and a blockchain network, like Ethereum, also has several millions (literally) at stake. So better have the design and the deployment right.
While researching for the publication, I came across this diagram shared by Vitalik a few months ago with how his plans for Ethereum 2.0 looked like. The diagram depicts the different areas of development and research, and the dependencies among them. A lot of exciting work ahead, and a lot of learning opportunities. When I was a kid, I always dreamed of building rockets and satellites, I may not have a chance to do so, but at least I am lucky enough to be working in a field as exciting as rocket science. See you next week!
Vitalik’s personal roadmap towards Eth2.0